개요
- 책을 보고 공부한 내용을 정리합니다.
딥러닝 텐서플로 교과서
- 저자 서지영님
- 길벗 출판사
코드 출처
https://github.com/gilbutITbook/080263
GitHub - gilbutITbook/080263
Contribute to gilbutITbook/080263 development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
9. 자연어 처리
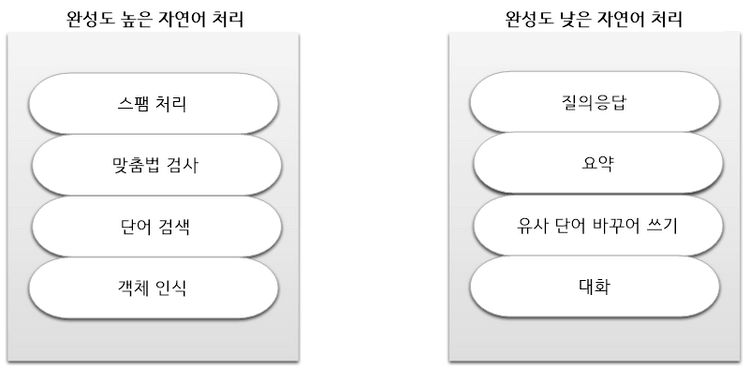
9.1.1 자연어 처리 용어 및 과정
1. 말뭉치(corpus)
- - 자연어 처리에서 모델을 학습시키기 위한 데이터
2. 토큰(token)
- 자연어 처리를 위한 문서는 작은 단위로 나누어야 함, 이떄 문서를 나누는 단위
- 문자열을 토큰으로 나누는 작업을 토큰 생성(tokenizing)
3. 토근화(tokenization)
- 텍스트를 문장이나 단어로 분리하는 것
4. 불용어(stop words)
- 문장 내에서 많이 등장하는 단어
- 분석과 관계 없으며, 자주 등장하는 빈도 때문에 성능에 영향을 미치므로 사전에 제거
5. 어간 추출(stemming)
- 단어를 기본 형태로 만드는 작업
- 예를들어 'cosign' ,'cosigned' 같은 단어를 'cosign'으로 통일
6. 품사 태깅(part -of -speech- tagging)
- 주어진 문장에서 품사를 식별하기 위해 붙여 주는 태그
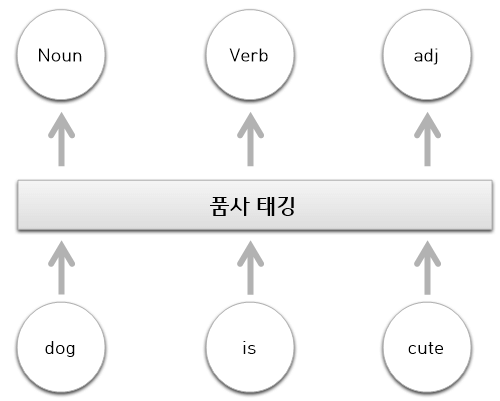
NLTK 이용
import nltk
nltk.download()
text= nltk.word_tokenize("Is is possible distinguishing cats and dogs)
'''
print(text)
결과: ["Is", "it", "possible", 'distingushing", 'cats', 'and', 'dogs]
'''
# 태깅에 필요한 자원 다운
nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger'
# 다운로드한 자원을 이용하여 품사를 태깅
nltk.pos_tag(text)
'''
[('Is', 'VBZ'),
('it', 'PRP'),
('possible', 'JJ'),
('distinguishing', 'VBG'),
('cats', 'NNS'),
('and', 'CC'),
('dogs', 'NNS')]
'''자연어 처리 과정
- 크게 4단계를 거침
- 인간 언어인 자연어가 입력 텍스트로 들어옴, 인간 언어가 다양하듯 처리 방식이 조금씩 다름
- 입력 테스트에 대한 전처리
- 전처리가 끝난 단어들을 임베딩. 즉, 단어를 벡터로 변환
- 분류 및 예측
9.1.2 자연어 처리를 위한 라이브러리
- NLTK
- 교육용으로 개발된 자연어 처리 및 문서 분석용 파이썬 라이브러리
- 제공 기능 : 말뭉치, 토큰생성, 형태소 분석, 품사 태깅
import nltk
nltk.download('punkt')
string1 = "my favorite subject is math"
string = "my favorite subject is math, english, economic and computer science"
nltk.word_tokenize(string1)
- Konlpy
from konlpy.tag import Komoran
komoran = Komoran()
# 형태소로 출력
print(komoran.morphs("나는 멋쟁이다, 멋쟁이가 아니다"))
# 품사 태깅
print(komoran.pos('나는 멋쟁이다, 멋쟁이가 아니다'))
- Gensim
- Word2Vec 라이브러리
- 주요 기능
- 임베딩, 토픽 모델링, LDA(Latent Dirichlet Allocation)
- 사이킷런
- 자연어 처리에서 특성 추출 용도로 많이 사용
- 주요 기능
- CountVectorizer : 텍스트에서 단어의 등장 횟수를 기준으로 특성 추출
- Tfidfvectorizer : TF-IDF 값을 사용해서 텍스트에서 특성 추출
- HashingVectorizer : CountVectorizer와 방법이 동일, 해시 함수 사용하여 실행시간 감소
9.2 전처리
- 딥러닝에서 사용하기 위해 전처리가 필요
- 전처리 과정
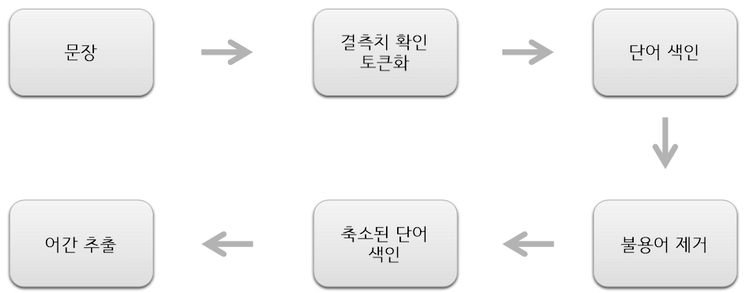
9.2.1 결측지 확인
- 결측지는 데이터셋에서 데이터가 없는(NaN) 것
# 결측지가 몇개인지 합산
df.isnull().sum()
# 결측지 비율
df.isnull().sum() /len(df)
# 모든 행이 NaN일 떄 삭제
df.dropna(how='all')
# NaN이 하나라도 있을 때 삭제
df.dropna()
# 결측지를 다른값으로 채우기
df.fillna(0)
# 결측지를 해당 열의 평균으로 채우기
df['x'].fillna(df['x'].mean())9.2.2 토큰화
- Tokenization(토큰화)는 주어진 텍스트를 단어/문자 단위로 자르는 것을 의미
1. 문장 토큰화
- 문장을 토큰화 한다는 것은 마침표(.), 느낌표(,), 물음표(?) 등 문장의 마지막을 뜻하는 기호에 따라 분리
from nltk import sent_tokenize
text_sample = 'fnknfkaflk asfjflaf afk, afkajfk'
token_sen = sent_tokenize(text_sample)2. 단어 토큰화
- 띄어쓰기를 기준으로 문장 구분
- 한국어는 띄어쓰기만으로 토큰을 구분하기 어려운 단점이 있음
from nltk import word_tokenize
words = word_tokenize(text_smaple)- 아포스트로피(')가 있는 문장 구분
from nltk.tokenize import WordPunctTokenizer
words = WordPunctTokenizer().tokenize(text_sample)- text_to_word(케라스 제공)
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import text_to_word_sequence
words = text_to_word_sequence(text_sample)9.2.3 불용어 제거
- 빈번하게 발생하여 의미를 부여하기 어려운 단어
- 예를 들어 'a', 'the' 같은 단어들은 모든 구문에 매우 많이 등장해서 의미가 없음
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
nltk.download('stopwords')
nltk.download('punkt')
sample_text = "One of the first things that we ask ourselves is what are the pros and cons of any task we perform."
text_tokens = word_tokenize(sample_text)
tokens_without_sw = [word for word in text_tokens if not word in stopwords.words('english')]
print("불용어 제거 미적용:", text_tokens, '\n')
print("불용어 제거 적용:", tokens_without_sw)
9.2.4 어간 추출
- 어간 추출(stemming)과 표제어 추출(lemmatization)은 단어 원형을 찾아줌
- 예를 들어 '쓰다'의 다양한 형태인 'writing', 'writes' ,'wrote'에서 'write' 찾음
- NLTK의 어간 추출로 대표적으로 Porter(포터)와 랭커스터(lancaster) 알고리즘 있음
1. 포터 알고리즘
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
stemmer = PorterStemmer()
print(stemmer.stem('obesses'), stemmer.stem('obssesed'))
print(stemmer.stem('standardizes'), stemmer.stem('standardization'))
print(stemmer.stem('national'), stemmer.stem('nation'))
print(stemmer.stem('absentness'), stemmer.stem('absently'))
print(stemmer.stem('tribalical'), stemmer.stem('tribalicalized'))
2. 랭커스터 알고리즘
from nltk.stem import LancasterStemmer
stemmer = LancasterStemmer()
print(stemmer.stem('obsesses'), stemmer.stem('obsessed'))
print(stemmer.stem('standardizes'), stemmer.stem('standardization'))
print(stemmer.stem('national'), stemmer.stem('nation'))
print(stemmer.stem('absentness'), stemmer.stem('absently'))
print(stemmer.stem('tribalical'), stemmer.stem('tribalicalized'))
- 포터 알고리즘과 다르게 랭커스터 알고리즘은 단어 원형을 알아볼 수 없을 정도로 축소시키기 떄문에 정밀도 낮음
3. 표제어 추출
- 일반적으로 어간 추출보다 표제어 추출의 성능이 더 좋음
- 품사와 같은 문법뿐만 아니라 문장내에서 단어 의미도 고려하기 떄문
- 어간 추출보다 시간이 더 걸림
- WorkNetLemmatizer()
import nltk
nltk.download('wordnet')
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
lemma = WordNetLemmatizer()
print(stemmer.stem('obsesses'), stemmer.stem('obsessed'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('standardizes'), lemma.lemmatize('standardization'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('national'), lemma.lemmatize('nation'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('absentness'), lemma.lemmatize('absently'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('tribalical'), lemma.lemmatize('tribalicalized'))
- 품사 정보 추가
- 앞 결과와 동일하지만 단어수가 많아지면 차이가 많이남
# 표제어 추출의 성능을 높이고자 단어에 대한 품사 정보 추가
print(lemma.lemmatize('obsesses','v'), lemma.lemmatize('obsessed','a'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('standardizes','v'), lemma.lemmatize('standardization','n'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('national','a'), lemma.lemmatize('nation','n'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('absentness','n'), lemma.lemmatize('absently','r'))
print(lemma.lemmatize('tribalical','a'), lemma.lemmatize('tribalicalized','v'))
9.2.5 정규화(normalization)
- 표현 방법이 다른 단어들을 통합해 같은 단어르 만들어 줌
- 예를 들어 USA와 US는 같은 의미로 해석되도록 만들어 줌
GitHub - heohyunjun/Sk_Shieldus: SK Infosec 클라우드 AI 융복합 과정
SK Infosec 클라우드 AI 융복합 과정. Contribute to heohyunjun/Sk_Shieldus development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'Study > 딥러닝 텐서플로 교과서 - 길벗' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Book]딥러닝 텐서플로 교과서[END] (0) | 2022.01.28 |
|---|---|
| [Book] 10. 자연어 처리를 위한 임베딩 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [Book]8. 성능 최적화 (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [Book]7. 시계열 분석 (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| [Book]6. 합성곱 신경망 2 (0) | 2022.01.04 |



